What Are Cranial Bones?
When you touch the top of your head, you are feeling the Cranial Bones, which form the main part of your skull. These bones create a strong shield around your brain, keeping it safe from injuries. They are hard, smooth, and perfectly shaped to fit together like puzzle pieces. Everyone should know that these bones are not just about shape they play a vital role in protecting one’s brain and helping other parts of the head work properly. Understanding them can help you appreciate how amazing the human body truly is.
Understanding the Skull’s Protective Framework
Your skull is not a single solid piece; it’s a combination of several bones joined together. Each part fits neatly, forming a tight barrier that guards your brain from external harm. One can think of it as nature’s helmet designed by evolution to give your brain maximum safety. These bones also support your eyes, ears, and nose, making it easier to perform daily actions like seeing, hearing, and smelling.
How Many Cranial Bones Are in the Human Skull?
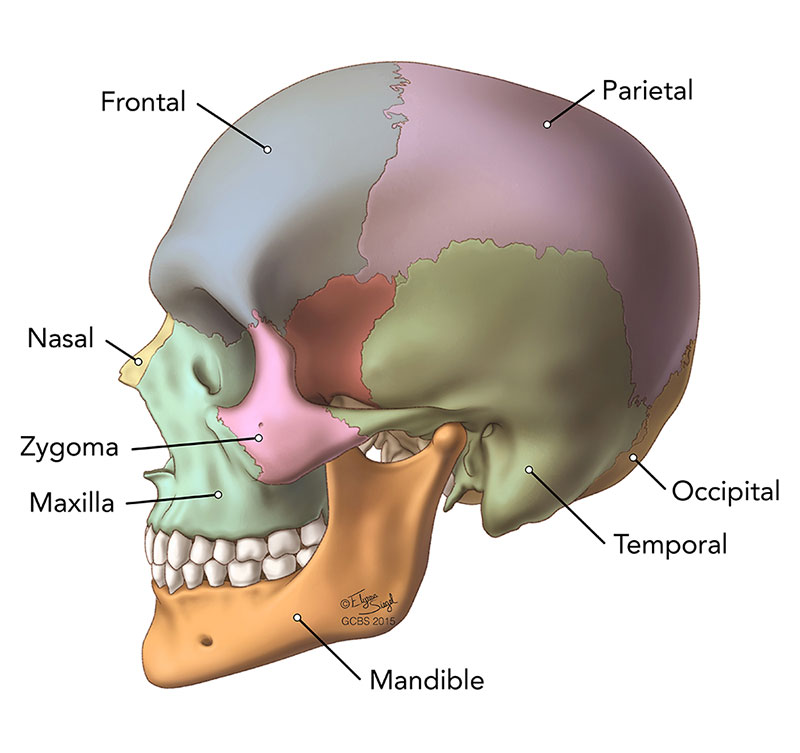
The human skull has eight cranial bones. Each one has a special function and location:
- Frontal bone – forms the forehead and upper part of the eyes.
- Parietal bones (2) – sit on the top and sides of your skull.
- Temporal bones (2) – found near your ears.
- Occipital bone – located at the back of your head.
- Sphenoid bone – sits in the middle of the skull, supporting other bones.
- Ethmoid bone – helps form the nasal cavity and the space between the eyes.
All these bones work together to protect your brain while maintaining the shape of your head.
Structure of Cranial Bones
Cranial bones are strong yet lightweight. They are made of compact bone on the outside and spongy bone inside. This design allows them to be both tough and slightly flexible. You can imagine it as a solid yet cushioned structure that absorbs shocks.
Each bone has edges known as sutures these are special joints that connect bones tightly without allowing movement. They act like stitching, keeping the skull firm and stable throughout life.
Expert Health Care Tips for Stronger Bone Health
When it comes to keeping your head and body healthy, you should always focus on preventive measures. Wear protective helmets during physical activities, maintain good posture, and eat a diet full of vitamins and minerals. Small steps like these can make a big difference in your long-term well-being. Health Care Tips such as regular checkups and balanced meals can help you stay safe from unexpected injuries and promote strong bones for years to come.
The Major Cranial Bones and Their Locations
To understand better, here’s how each bone fits:
- The frontal bone forms your forehead and protects the front part of your brain.
- The parietal bones make up the top and sides, joining together at the top of the head.
- The temporal bones are found around your ears and help protect the hearing organs.
- The occipital bone is at the back, covering the area that controls vision and movement.
All these bones connect in a way that allows your skull to maintain its round, smooth structure.
How Cranial Bones Connect and Form the Skull
The cranial bones are joined by fibrous joints called sutures. These joints are immovable, which means they hold the skull tightly. When you are a baby, these sutures are flexible and allow your head to grow. As one grows older, they become harder and more solid. This process ensures that your skull remains strong enough to protect your brain while giving it the shape it needs.
Functions of Cranial Bones
The main purpose of these bones is protection. Your brain is delicate and soft, so it must be covered by something strong. These bones also provide support for your facial features and give a base for muscles to attach. Every time you chew, talk, or smile, these bones play a hidden role in helping those movements happen smoothly.
They also form cavities that hold and safeguard sensory organs like the eyes and ears. Without them, you wouldn’t be able to see, hear, or even maintain your sense of balance properly.
Protecting the Brain and Sensory Organs
Cranial bones act like a natural helmet, protecting the most sensitive part of your body. They create layers around the brain and separate it from harmful shocks or impacts. Even a small accident could harm the brain if these bones didn’t exist. That’s why wearing extra protection, like helmets during activities such as biking, is still essential even though your skull already provides natural safety.
Supporting Facial Muscles and Movements
Besides protection, these bones also give shape to your face. They support muscles used for expressions, speech, and chewing. For instance, when you smile or frown, the muscles pull on the bones, allowing your face to move smoothly. Without this structure, you wouldn’t be able to make expressions or talk properly.
Anatomy of the Human Skull
The skull is divided into two main parts the cranial part and the facial part. The cranial part holds and protects the brain, while the facial part supports the mouth, eyes, and nose. The two are closely connected through joints, forming a solid and balanced structure.
The Role of Joints and Sutures in the Skull
Sutures connect the cranial bones and prevent unwanted movement. These joints allow the skull to expand during growth in childhood. Once you reach adulthood, they close firmly. This closure ensures maximum protection and stability.
Differences Between Cranial and Facial Bones
Many people confuse cranial bones with facial bones. Cranial bones protect the brain, while facial bones support the features of the face. The facial bones include the jaw, cheekbones, and nasal bones, which help with breathing and eating. Both groups are essential for a complete skull structure.
Why Understanding Cranial Bones Is Important
Knowing about cranial bones helps you understand how your body works. They are more than just hard shells they play a life-saving role. Doctors study these bones to identify fractures, diseases, or injuries that can affect the brain. By learning about them, one can also recognize the importance of taking proper care of the head to prevent trauma.
Common Skull Injuries and How They Affect the Brain
A hard fall or a severe hit can cause cracks or fractures in the skull. These injuries might look small from outside but can be dangerous inside. They may lead to bleeding, swelling, or brain injury. That’s why one must always use safety gear while driving, biking, or playing sports.
How to Keep Your Skull and Brain Healthy
Your skull’s strength depends on your bone health. Eating calcium-rich foods, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly can help maintain healthy bones. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol also helps strengthen bone density over time.
Final Thoughts on Cranial Bones
The skull might look simple from the outside, but inside, it’s a masterpiece of design and protection. Its eight cranial bones work together like a perfect shield for your brain. Understanding their structure and purpose helps you value how much care your body takes to protect you every second. You don’t need to be a doctor to realize that good bone health is vital all you need is awareness and the willingness to protect what keeps you alive.